 |
| Here We Go |
 |
| Question 5 |
a) The connective tissue underneath the skin is a clear, stretchy,
gel like substance. It was for the most part easily separated; except for
certain places where is was “anchored and I had to cut it.
b) The connective tissue under the skin was adipose tissue.
 |
| Question 6 |
a) The fat is lumpy and excretes a fluid when squeezed.
b) The fat stores energy and serves as a layer of insulation.
c) The biological term for the type of cells that store fat are lipids.
 |
| Question 8 |
a) There is a large muscle covering the outside and underneath are a series of smaller muscles each attached to a tendon. Amount these are little pockets of fatty tissue.
b) There are many muscles present.
c) The muscle were bundled together and attached by the adipose tissue.
d) The muscle were arranged in a way that they or the tendons did not interfere with each other as they moved.
 |
| Question 9 |
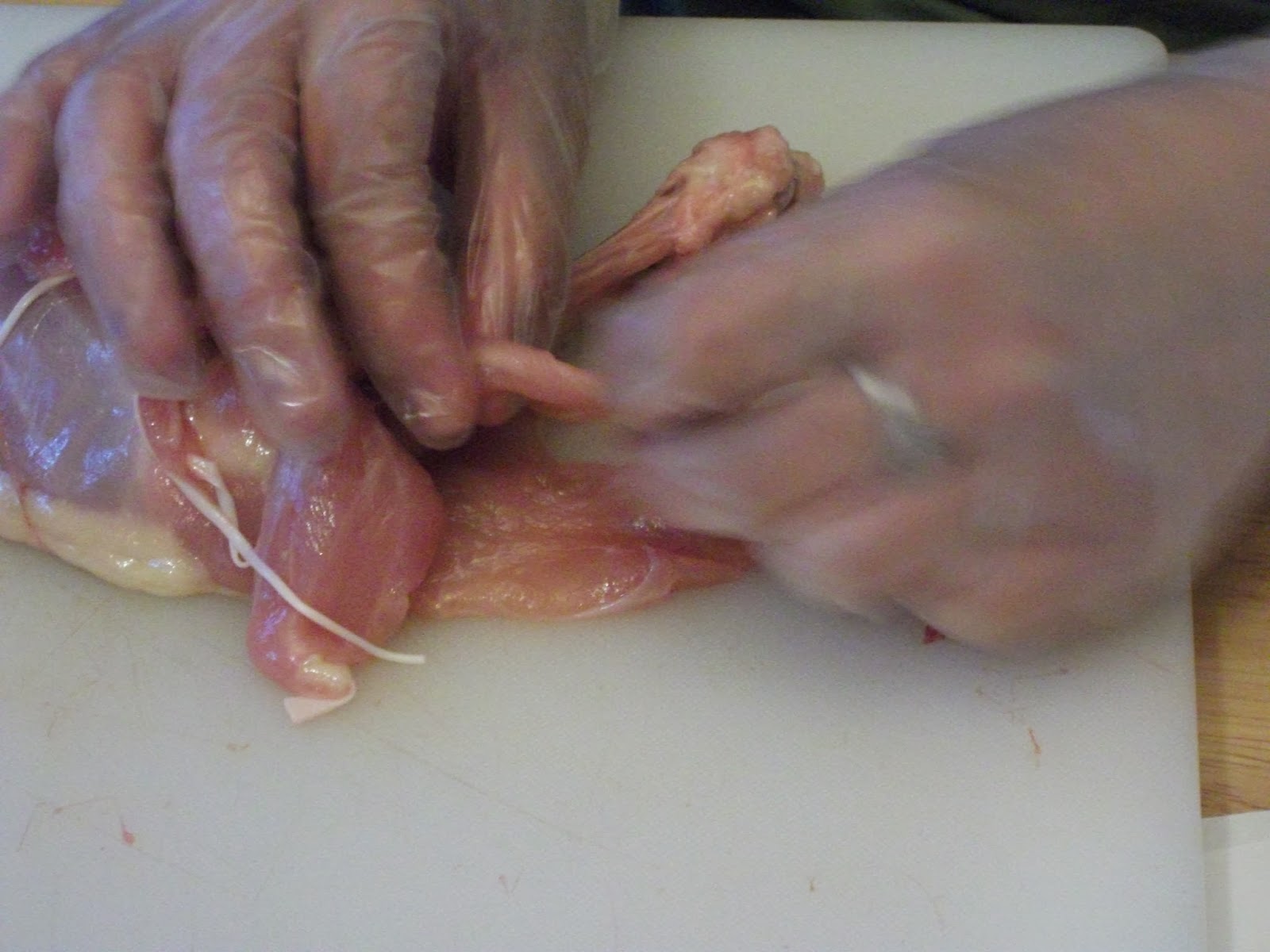
a) Tendons are composed of dense fibrose connective tissue.
 |
| Question 10 |
a) The skeletal muscles connect to the tendons, which attach to bones.
b) They are voluntary muscles attached to nerves that activate the muscles to move the limb.
 |
| Question 11 |
a) I was able to find the nerve.
 |
| Question 12 |
a) Ligaments are composed of dense connective tissue.
 |
| Question 16 |
a) The knee joint is a synovial joint.
b)Bending the knee joint is extension.
Question 18
a) Inside to the bone we would find a soft material called red bone marrow.
Question 17
a) The texture at the end of the bones at the joint is smooth.
b) The name of this connective tissue is cartilage.
c) When the cartilage wears away the bones make contact cause pain while walking.
d0 To delay this wear the knee has a thin fluid filled cavity called the bursa.
a) Inside to the bone we would find a soft material called red bone marrow.
b) The following are thee specific types of cells: 1)osteocytes, 2)stem cells, and 3)yellow bone marrow.
c) The following are three functions of bones: 1) to give living things shape, 2) to allow more efficient movement, and 3) to protect vital organs.
Thank you I really had fun.
ReplyDelete